
Molecular basis of inheritance: Initiator and terminator codon. The lac operon ( lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Molecular basis of inheritance: The DNA-structure of polynucleotide chain, central dogma. It is produced by the 'a' structural gene of the lac operon. (biochemistry) Any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of an acetyl group from one molecule to another. RNA polymerase transcribes DNA to mRNA which is ultimately translated into a functional protein.įurthermore, what is the function of Transacetylase in lac operon?

Promoters are a vital component of expression vectors because they control the binding of RNA polymerase to DNA. RepA has a dual function: as a dimer, it binds to an inversely-repeated sequence acting as a repressor of its own. A promoter is a region of DNA where transcription of a gene is initiated. RepA is the DNA replication initiator protein of the Pseudomonas plasmid pPS10. The resulting transcription produces an RNA molecule (such as mRNA). The function of the operator within genetics is to regulate the production of a certain portion of the DNA.Īlso Know, what is the function of the promoter? Definition. A promoter, as related to genomics, is a region of DNA upstream of a gene where relevant proteins (such as RNA polymerase and transcription factors) bind to initiate transcription of that gene. The gene, or genes, which get transcribed when the operator is bound are known as the operon.
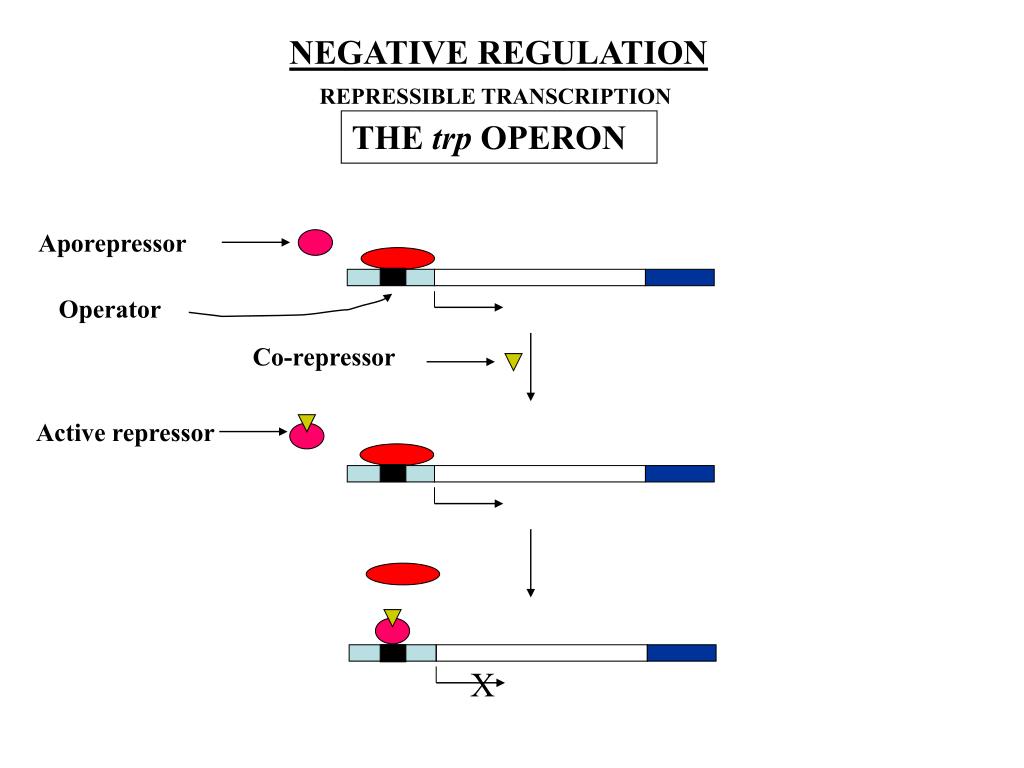
A promoter is like a doorknob, in that the promoters of many operons are similar.įurthermore, what is the function of the operator in an operon?Īn operator is a genetic sequence which allows proteins responsible for transcription to attach to the DNA sequence. The operator is a short region of DNA that lies partially within the promoter and that interacts with a regulatory protein that controls the transcription of the operon.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
